World
AIDS Day observes on the 1st December each year.It is an occasion for all the
people in the world to unite in the fight against HIV, to show support for
people living with HIV, and to mourn those who have died from a AIDS-related
illness. 2018 will be making its 30th anniversary of World AIDS Day on 1
December. This year’s theme for World AIDS Day is “Know your status”.
Global
HIV & AIDS Statictics
In
2017, 36.9 million [31.1 million–43.9 million] people globally were living with
HIV and 21.7 million million people were accessing anti-retroviral therapy.1.8
million people became newly infected with HIV and 940 000 people died from
AIDS-related illnesses. Every week, around 7000 young women aged 15–24 years
become infected with HIV.The risk of acquiring HIV is 27 times higher among men
who have sex with men; 23 times higher among people who inject drugs; 13 times
higher for female sex workers; 12 times higher for transgender women. TB
remains the leading cause of death among people living with HIV and TB accounts
for around one in three AIDS-related deaths. In 2016, 10.4 million people
developed TB disease and 1.2 million were living with HIV. People living with
HIV with no TB symptoms need TB preventative therapy, which lessens the risk of
developing TB and reduces TB/HIV death rates by around 40%.
Epidemiological
context of HIV in Myanmar
The
HIV epidemic in Myanmar began with the identification of the first HIV infected
case in 1988, and the almost three decades old HIV epidemic is concentrated
among population subgroups with high-risk behavior. These population subgroups
include Female Sex Worker (FSW), Men who have sex with Men (MSM), People Who
Inject Drug (PWID), and sexual partners of these sub-group populations. Myanmar
is one of the few countries in the world where the incidence rate of HIV
infection among adult 15 to 49 years old has decreased by more than fifty per
cent over the last decade (Ending AIDS, global AIDS update, UNAIDS, 2017).
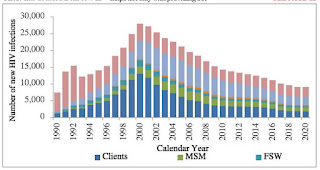
According
to estimation and projection exercise employing the AIDS Epidemic Modelling,
the new HIV infections among people aged 15 and above reached the peak at
around 28,000 in the year 2000 which was declined to 12,500 in 2015 and further
declined to 11,000 in 2017. The risk groups including Key affected populations
(KAPs) shared more than seventy per cent of annual new infections in 2017.
However,
the HIV Epidemic at sub-national level is quite different from region to region.
At national level, all modes of transmission are important, but at sub-national
level there are some key modes of transmission driving the epidemic: Kachin
State, Shan  (N) State and Sagaing Region have an Injecting
Drug Use (IDU) driven HIV epidemic whereas Yangon and Mandalay regions have Men
that Have Sex with Men (MSM) and heterosexual driven (FSW and clients)
epidemic.
(N) State and Sagaing Region have an Injecting
Drug Use (IDU) driven HIV epidemic whereas Yangon and Mandalay regions have Men
that Have Sex with Men (MSM) and heterosexual driven (FSW and clients)
epidemic.
Progress
in National Responses to HIV
The
national response against HIV/AIDS has been implementing in concerted efforts
with all implementing partners including WHO, UN organizations, NGOs and
community based organizations, and positive groups since the early phase of the
epidemic.
The
efforts are guided by the medium (5-year) and long term National Strategic
Plans (NSP) for HIV/AIDS which have been developed based on the information
from program evaluations, surveillance surveys, operational researches and
other studies and with the full engagement of stakeholders.
Myanmar’s
current National Strategic Plan on HIV and AIDS (2016-20) envisioned the
political declaration on ending HIV as public health problem by 2030 where the
fast track 90-90-90 prevention, testing and treatment targets are adopted as
built in strategic milestones assessing the progress of national responses.
The
National Strategic Plans are usually used as a guideline that ensuring
concerted efforts of all stakeholders. The current cycle of NSP has based on
five main strategic directions aiming for providing holistic and continuum of
services while moving towards the goal of “reducing HIV transmission and HIV
related morbidity, mortality, disability, & social and economic impact”
Reducing
new HIV infection and Improving health outcomes for all people living with HIV
in Myanmar
The
significant reduction in the number of new infection in the past decade
revealed the positive impact of prevention services. Of the estimated 66,000
FSW (NAP, 2017), the proportion reached with prevention program was 63% in
2017. In 2011, 37% of the estimated 252,000 MSM (NAP, 2017) was reached by
prevention services in 2017. The number of PWID was estimated to be 83,000
(NAP, IBBS PWID 2015). 72% of PWID accessed harm reduction services in 2017
while the number receiving MMT was increased from 10,290 at the end of 2015 to
13,441 by the end of 2017. In addition, the number of needle syringes
distributed a PWID per annum have been increased to 324 in 2017.
Services
for improving health outcomes for people living with HIV have been increasing
reach in term of both geographic and population coverage. Coverage of
antiretroviral therapy (ART) has doubled from 55% in 2015 to 66% (146,826 of
estimated 223,000 PLHIV) on ART by 2017.
In
addition, the treatment and care services have been made available to more and
more townships by expanding the ART centers and establishing decentralize ART
services up to sub township level. By the end of 2017, the treatment and care
services are available in 227 townships through 127 ART centers and 174
decentralized sites. In addition, ART services are increasingly available and
accessible for those in prisons. In collaboration with National TB control
program, 96% of PLHIV enrolled in care received TB screening in 2016 which
increased from 95% in 2013.
Regarding
Progress in Strengthening integration of community and health systems and
promoting a human right based approach, innovative services delivery modalities
that help integration of community based services and ensure continuum of
services from prevention, testing, to enrollment into care was formalized and
started rolling out in townships with high priority townships as defined in NSP
III. There are ongoing activities for strengthening procurement and logistics
management, and laboratory information system in recent years. Review and
revision of HIV related laws/policies including the new HIV laws, the amendment
of the Prostitution act and are also in progress.
Regarding
Progress in Strengthening strategic information and research to guide service
delivery, management and policy, a programmatic exercise for key populations
that helps not only with providing better picture of program needs but also
improve capacity of local stakeholders for better coordination and optimized
resources allocation was conducted in 46 highest burden townships in 2016 and
in additional 28 townships in 2017. Details HIV Epidemic picture are available
for Yangon, Mandalay, Kachin, Shan (North) and Sagaing.
Regarding
Progress in Promoting accountable leadership for the delivery of results and
financing a sustainable response, under the leadership of Myanmar Health Sector
Coordinating Mechanism (M-HSCC), the HIV Technical Strategic Group (HIV-TSG)
has being fully functioning ensuring the cooperative responses from all
implementing partners, drawing technical inputs from UN agencies and
development partners, and acquisitive funding opportunities from government and
development partners.
The
way forward
Myanmar
has already announced to join “the Global HIV Prevention Coalition” during the
71st World Health Assembly on May 22,2018, in Geneva, Switzerland.Union
Minister for Health and Sports Dr Myint Htwe mentioned that Myanmar is creating
an enabling environment for providing continuous efforts for removing legal,
stigmatizing factors and financial barriers to help achieve “AIDS FREE MYANMAR”
Although
Myanmar has limited resources in both Central NAP and State/Regional AIDS/STD
teams the following activities are planned as priorities among others in the
coming years.
√
Strengthen prevention of new infections ensuring the holistic continuum of
services for all key population and achieving the elimination of mother to
child transmission of HIV in Myanmar by 2025.
Devising
innovative service delivery models that tailored to the local epidemic and need
Improve
the accessibility of lab services for all and strengthen the lab information
system that ensure the results are linked and used to improve individual
patient management
To
holistically provide HIV health services to target communities and populations
by way of providing medical facilities, equipments, strengthening capacity of
health workers at national level, State or Regional and townships, improved
access to community outreach among target populations and encourage HIV
infected person to approach those facilities and workers.
Know
your status
HIV
testing is extremely important for expanding treatment and making sure that all
people living with HIV can lead healthy and productive lives.It is also
essential to achieving NAP targets and enabling people to make choices about
HIV prevention so they can protect themselves and their love ones.
Globally,
75% of all people living with HIV knew their HIV status in 2017. In Myanmar, an
increasing trend can be seen in term of HIV testing coverage among key
populations. The testing coverage increased from 42% in 2015 to 60% in 2017 for
FSW; from 13% in 2015 to 33% in 2017 for MSM; and from 33% in 2015 to 43% in
2017 for PWID. In addition, efforts have been made to reach the partners of key
populations. There has been increase in number of partners being reached with
HIV prevention services and HIV tests. .
Myanmar
has fully followed the Global Goal of Ending Paediatric HIV infection by 2020
and prolonging mother life. Establishing a community based service delivery
modality is a priority recommendation to reach the Global PMCT Goal effectively
and sustainably (WHO,2013). In late 2013, Myanmar started its first step of
community based movement with the introduction of decentralized HIV testing
where the primary care providers are allowed to perform screening test for all
pregnant women seeking Antenatal Care.
This
community based testing strategy brought a significant improvement in the
number of pregnant women received HIV test and test result (309,677 pregnant
women knew HIV status in 2013 and it was increased to 848,557 in 2017).
Although
improvements have been seen in term of providing HIV testing and treatment for
positive pregnant women living with HIV, limited improvement has been observed
in the area of providing follow up care and diagnostic services for exposed
infants. Only 28% of the exposed infants received HIV testing within 2 months
of age (early infant diagnosis) in 2017.
Regarding
HIV testing, some barriers such as Stigma, discrimination and access to
confidential HIV testing still persist.
World
AIDS Day 2018 theme emboldens everyone to know their HIV Status.
You
can join us in the fight this World AIDS Day in promoting awareness about the
importance of knowing one’s status and asking for the removal of all barriers
to accessing HIV testing.
Reference:
1.
Draft Progress Report 2018, National AIDS Program, DOPH, MOHS, 2018
2.
Global HIV & AIDS Statistics-2018 fact sheet, UNAIDS, 2018
3.
National Strategic Plan on HIV and AIDS, Myanmar(2016-2020), DOPH, MOHS,2016
4.
World AIDS Day 2018 Message of UNAIDS Executive Director, UNAIDS,2018
5.
World AIDS Day 2018-Feature Story, UNAIDS, 2018
By
Dr Aung Tun, Dr Htun Nyunt Oo
Ref; The Global New Light of Myanmar
Ref; The Global New Light of Myanmar


No comments:
Post a Comment